In the dynamic world of fashion and textile, CO₂ laser technology has emerged as a revolutionary force. It offers a wide range of applications that enhance creativity, precision, and efficiency. CO₂ lasers emit infrared light at a wavelength of around 10.6 micrometers, which is highly absorbed by many textile materials, making them ideal for various processing tasks.
Cutting Applications
1. Precision Cutting
Fabric Cutting: CO₂ lasers can precisely cut a vast array of fabrics, from delicate silks and chiffons to heavy-duty denim and wool. For example, in high-end fashion brands, laser cutting is used to create intricate patterns for evening gowns. The laser beam acts as a “knife” with extremely fine focus, allowing for cuts with minimal fraying. This is especially important for fabrics that are prone to unraveling, as it eliminates the need for additional finishing steps such as hemming in some cases.
Leather Cutting: In the production of leather goods like handbags, shoes, and jackets, CO₂ lasers provide clean and accurate cuts. They can cut through different thicknesses of leather, from thin lambskin to thick cowhide. The laser’s non-contact nature prevents damage to the leather surface and maintains its natural texture and quality.
2. Intricate Designs
Lace and Embellishments: CO₂ lasers can cut lace patterns with a level of detail that is difficult to achieve with traditional methods. Designers can create unique lace motifs, including geometric shapes, floral patterns, and abstract designs. These laser-cut laces can be used as trimmings on dresses, blouses, and lingerie, adding a touch of elegance and sophistication.
Cut-out Details: In fashion, cut-out details have become a popular trend. CO₂ lasers can precisely cut out shapes in fabrics, creating eye-catching designs. For instance, on a denim jacket, laser-cut star-shaped holes can be added to give it a trendy and edgy look.
Engraving Applications
1. Branding and Logo Engraving
Textile Products: CO₂ lasers can engrave brand names, logos, and labels directly onto textile products. This provides a permanent and high-quality branding solution. For example, a sportswear brand can engrave its logo on the front of a T-shirt. The engraved logo has a sharp and professional appearance, and it is more durable compared to printed logos, which may fade over time.
Leather Goods: In the leather industry, laser engraving is used to add brand identity to products. Luxury leather handbag brands often engrave their logos on the surface of the bags, creating a luxurious and exclusive look. The engraving can be done with different depths and styles, depending on the design requirements.
2. Decorative Engraving
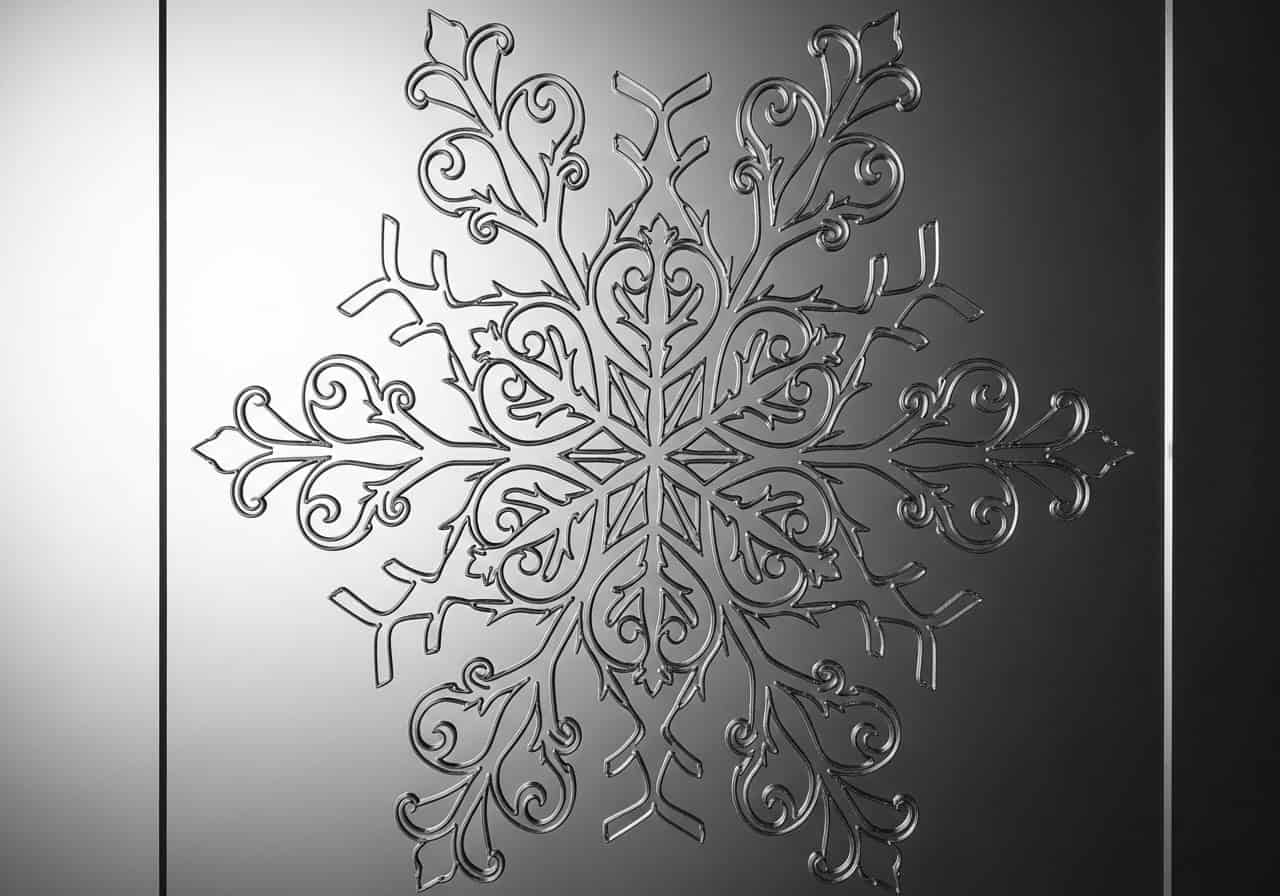
Pattern Creation: CO₂ lasers can create decorative patterns on textiles and leather. These patterns can range from simple geometric patterns to complex, hand-drawn-like designs. For example, on a silk scarf, a laser can engrave a beautiful paisley pattern, enhancing its aesthetic appeal. The engraved patterns can be used to add a unique touch to mass-produced products or to create one-of-a-kind pieces.
Perforation Applications
1. Breathability Enhancement
Sportswear and Activewear: In sportswear and activewear, CO₂ lasers are used to perforate fabrics to improve breathability. For example, on a running shirt, laser – perforated holes can be added in areas where the body sweats the most, such as the underarms and back. These perforations allow air to circulate, keeping the wearer cool and comfortable during physical activities.
2. Decorative Perforation
Fashion Accessories: Perforation can also be used as a decorative element in fashion accessories. For example, on a leather belt, laser-perforated holes can be arranged in a decorative pattern, adding a stylish touch to the accessory.
Advantages of CO₂ Laser in Fashion and Textile
1. Precision and Accuracy
CO₂ lasers offer extremely high precision and accuracy, allowing for the creation of detailed and complex designs. This is crucial in the fashion and textile industry, where even the smallest design element can make a big difference in the overall look of a product.
2. Flexibility
CO₂ laser cutting machines can be used on a wide variety of materials, including different types of fabrics, leather, and synthetic materials. Additionally, the laser parameters can be easily adjusted to achieve different cutting, engraving, and perforation effects, providing designers with great flexibility in their creative process.
3. Efficiency
Laser processing is a fast and efficient method. It can significantly reduce production time compared to traditional manual or mechanical methods. For example, cutting multiple pieces of fabric with a laser can be done much quicker than using a pair of scissors or a mechanical cutter.
4. Environmental Friendliness
CO₂ laser processing is a relatively clean and environmentally friendly technology. It does not require the use of chemicals or large amounts of water, which is beneficial for reducing the environmental impact of the fashion and textile industry.
Challenges and Future Developments
1. Challenges
Material Compatibility: Some materials may not respond well to CO₂ laser processing. For example, certain synthetic fibers may melt or produce toxic fumes when exposed to the laser. Manufacturers need to carefully select materials and adjust laser parameters to ensure optimal results.
Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and installing a CO₂ laser system can be relatively high, which may be a barrier for small-scale fashion and textile businesses.
2. Future Developments
Improved Material Compatibility: Research is being conducted to improve the compatibility of CO₂ lasers with a wider range of materials. This may involve the development of new laser – absorbing coatings or the modification of existing materials to make them more suitable for laser processing.
Integration with Digital Design: In the future, CO₂ laser systems are likely to be more closely integrated with digital design software. This will allow designers to directly transfer their digital designs to the laser system, enabling faster and more accurate production.
Automation and Robotics: The use of automation and robotics in CO₂ laser processing is expected to increase. This will further improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs, making laser – processed fashion and textile products more accessible to a wider market.
In conclusion, CO₂ laser technology has already made a significant impact on the fashion and textile industry, and its potential for future development is vast. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely to play an even more important role in shaping the future of fashion and textile production.
The future trends in CO₂ laser applications for fashion and textiles are diverse and promising, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer demands, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Here are some key trends:
1. Enhanced Precision and Complexity in Design
Micro-scale Patterns: Future CO₂ lasers will be capable of creating even more intricate and micro-scale patterns on fabrics and textiles. This could include patterns with details at the sub-millimeter level, enabling designers to push the boundaries of what is currently possible in terms of visual complexity and aesthetic appeal. For example, creating microscopic floral patterns on silk scarves or detailed geometric designs on high-end evening gowns.
3D and Multi-layer Designs: There will be an increasing focus on 3D laser processing in the fashion and textile industry. CO₂ lasers may be used to create multi-layer and three-dimensional structures within fabrics, such as raised patterns, embossed textures, and complex volumetric designs. This could revolutionize the way garments and textile products are perceived and worn, adding a new dimension to fashion design.
2. Integration with Digital Technologies
CAD/CAM Integration: The integration of CO₂ laser systems with computer – aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software will become even more seamless. Designers will be able to directly transfer their digital designs to the laser system, allowing for faster and more accurate production. Additionally, real-time design modifications can be made during the production process, reducing lead times and increasing flexibility.
AI-Driven Design and Processing: Artificial intelligence (AI) will play a significant role in CO₂ laser applications. AI algorithms can analyze fabric properties, design requirements, and laser parameters to optimize the cutting, engraving, and perforation processes. For example, AI can predict the best laser settings for a particular fabric and design combination, ensuring high-quality results and minimizing material waste.
3. Sustainable and Eco-friendly Solutions
Reduced Material Waste: CO₂ laser technology will continue to contribute to reducing material waste in the fashion and textile industry. With more precise cutting and engraving capabilities, manufacturers can maximize the use of fabric and minimize off – cuts. Additionally, the ability to create custom designs with lasers means that products can be made to order, reducing overproduction and inventory waste.
Use of Sustainable Materials: As the demand for sustainable fashion grows, CO₂ lasers will be increasingly used to process eco – friendly materials such as organic cotton, bamboo, and recycled synthetics. The non – chemical nature of laser processing makes it an ideal technology for working with these sensitive materials, ensuring that the environmental benefits of the materials are maintained throughout the production process.
4. Customization and Personalization
On-demand Production: Consumers are increasingly seeking personalized and unique fashion items. CO₂ lasers enable on-demand production, allowing manufacturers to quickly and easily produce customized products. For example, a customer could choose a design, pattern, or logo, and the laser system could produce a one-of-a- kind garment or textile accessory within a short time frame.
Personalized Textile Art: CO₂ lasers will also facilitate the creation of personalized textile art. Artists and designers can use lasers to create custom-made wall hangings, tapestries, and other textile art pieces, tailored to the specific preferences and spaces of individual customers.
5. Automation and Robotics
Automated Production Lines: The use of automation and robotics in CO₂ laser processing will become more widespread. Automated conveyor systems can transport fabrics and textiles through the laser processing area, while robotic arms can handle and position the materials with high precision. This will increase production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve the consistency of the final products.
Collaborative Robots: Collaborative robots, or cobots, will work alongside human operators in the fashion and textile industry. Cobots can assist with tasks such as loading and unloading materials, adjusting laser parameters, and quality control. This combination of human creativity and robotic precision will lead to more efficient and innovative production processes.
6. New Material Applications
Smart Textiles: CO₂ lasers will be used to process smart textiles, which incorporate electronic components, sensors, and conductive materials. The lasers can be used to cut and pattern these materials without damaging their functionality, enabling the integration of technology into fashion and textile products. For example, creating wearable devices with laser – cut fabric components that can monitor vital signs or interact with mobile devices.
Nanofiber and Biomaterial Processing: With the development of new materials such as nanofibers and biomaterials in the textile industry, CO₂ lasers will find new applications. These lasers can be used to process these advanced materials, creating unique properties and functionalities in fabrics and textiles, such as enhanced filtration, antibacterial properties, or biodegradability.